What are the differences between CMYK, PMS, RAL, RGB and HEX colors?
October 14, 2025
Rob de Melker

Colors are essential in design and communication. Yet we often notice confusion about the different color codes and systems: CMYK, PMS, RAL, RGB, and HEX. Each system has its own purpose and ideal use case. In this article, we explain what the differences are, why they matter, and when to use each one.
What do CMYK, PMS, RAL, RGB, and HEX stand for?
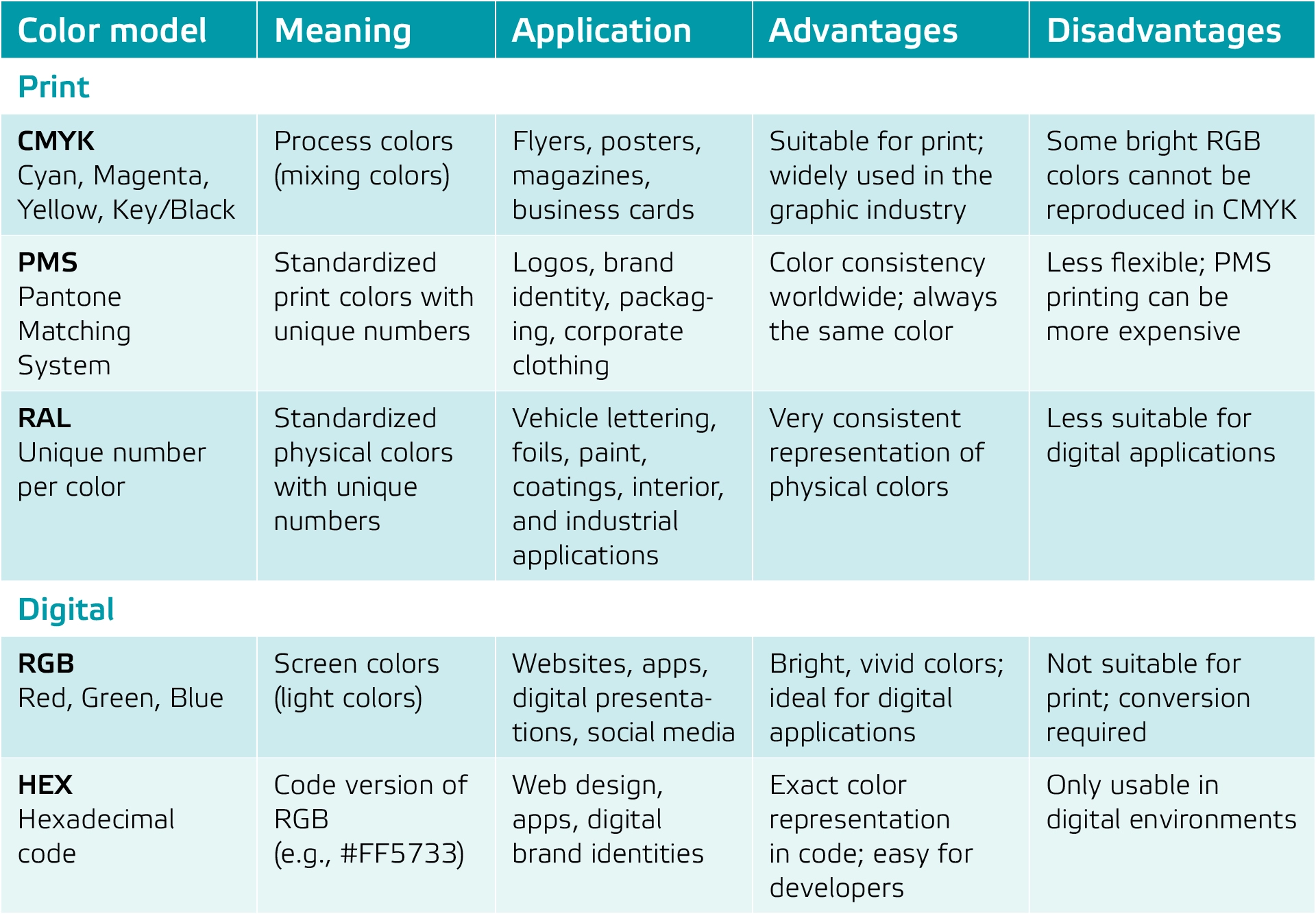
CMYK
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black). This color model is used for print. Printers mix these four base colors to create a wide range of colors. The downside: not all colors you see on your screen can be reproduced exactly in CMYK.
PMS
PMS stands for Pantone Matching System. This is a standardized system in which each color is assigned a unique number. PMS colors are mainly used in branding and print work where exact color consistency is crucial, such as logos, letterheads, or packaging.
RAL
RAL is a European color coding system widely used in industry, paint, construction, and interior design. Each RAL color has a unique number (such as RAL 9010 or RAL 3020) that corresponds to a specific, physically measured shade. RAL is primarily used for paints, coatings, and varnishes, but also for applications such as vehicle graphics and adhesive films, ensuring that materials have the same color in practice — regardless of manufacturer or product type.
RGB
RGB stands for Red, Green, Blue. This color model is used for anything that emits light, such as computer screens, TVs, and phones. Colors are created by mixing light: the more light, the brighter the color.
HEX
HEX is a hexadecimal code primarily used in web design. It is essentially a way to represent RGB colors in code, for example #FF5733. This makes it easy for developers to apply exact colors to websites or apps.
Why the difference matters
Using the wrong color models can lead to significant differences in how colors appear.
A logo that looks perfect on your screen in RGB can suddenly appear dull or off in print. PMS and RAL ensure consistent colors in physical applications, while HEX is important for displaying colors accurately online. Choosing the right model helps avoid disappointments and maintains a professional appearance.
Examples of how to use each color model
CMYK – Print
Flyers, posters, magazines, business cards. Because this model is specifically tailored for printers, it is the standard in the graphic design industry.
PMS – Branding and Corporate Identity
Logos, business cards, packaging, company uniforms. PMS is used when a brand needs to maintain the exact same color, regardless of the printing process.
RAL – Paint, Interior, Production, and Vehicle Applications
Coatings, wall paint, furniture, vehicles, vehicle graphics, adhesive films, and industrial applications. RAL ensures that physical materials have the same color in practice, regardless of manufacturer or surface.
RGB – Digital Media
Websites, social media, presentations, screen designs. Everything viewed on a screen is based on RGB.
HEX – Web Design and Digital Applications
Websites and apps. HEX codes ensure colors are displayed accurately and consistently in CSS and HTML.

What are the risks of using colors incorrectly?
Ignoring the correct color model can lead to:
- Color inconsistencies: A vibrant blue brand color may appear dull or grayish in print.
- Unprofessional appearance: Different shades of your brand logo across print, online, and physical materials create an inconsistent impression.
- Loss of brand recognition:
A classic example: a brand that prints its RGB logo directly without converting it to CMYK often ends up with a final result that visibly differs from the original brand style.
Checklist: How do you choose the right color model?
- Are you designing for print? Use CMYK or PMS.
- Are you designing for a website or app? Use RGB or HEX.
- Working with paint, coatings, foils, or other physical materials? Use RAL.
- Want your brand color to always look exactly the same? Choose PMS or RAL as your reference.
- Working cross-media (both print and online)? Define CMYK, HEX, and optionally RAL codes in your brand style guide.
Conclusion
CMYK, PMS, RAL, RGB, and HEX are not interchangeable systems — each was developed for a specific purpose.
By understanding where and when to use them, you ensure a consistent and professional appearance for your brand across online, print, and physical applications.

Author of this blog
Rob de Melker
Rob has many years of experience in the graphic design industry and leads the team that creates professional websites, logos, brand identities, and web applications, with additional expertise in animations and lettering. He is known for his personal approach: a cup of coffee always leads to better advice than communicating only by email or messaging. Clients trust him for creative and technical solutions that truly work.
Do you not check our website daily for the latest tips? No problem! You can also follow us on our social media channels. We regularly share updates, useful facts and a behind-the-scenes.